Central dogma and genetic medicine biointeractive answer key – Unveiling the Central Dogma and Genetic Medicine: A Comprehensive Guide
The central dogma of molecular biology, a cornerstone of genetics, governs the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein. This understanding has revolutionized genetic medicine, leading to groundbreaking advancements in medical treatments. This guide delves into the intricacies of the central dogma, its applications in genetic medicine, and the Biointeractive Answer Key resource, providing a comprehensive overview of this pivotal concept.
Central Dogma Overview
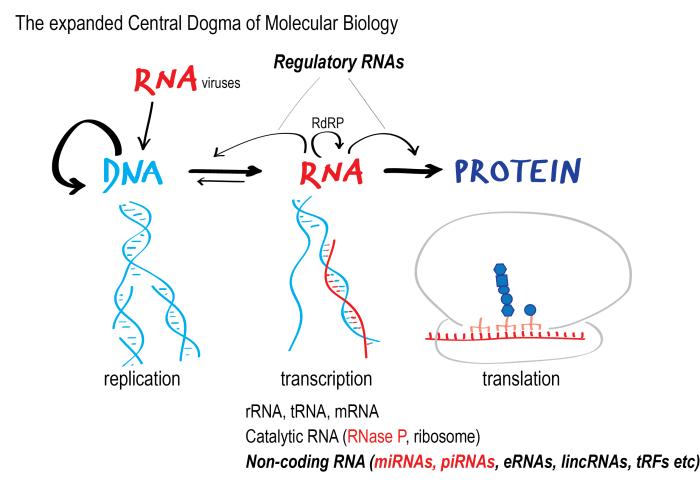
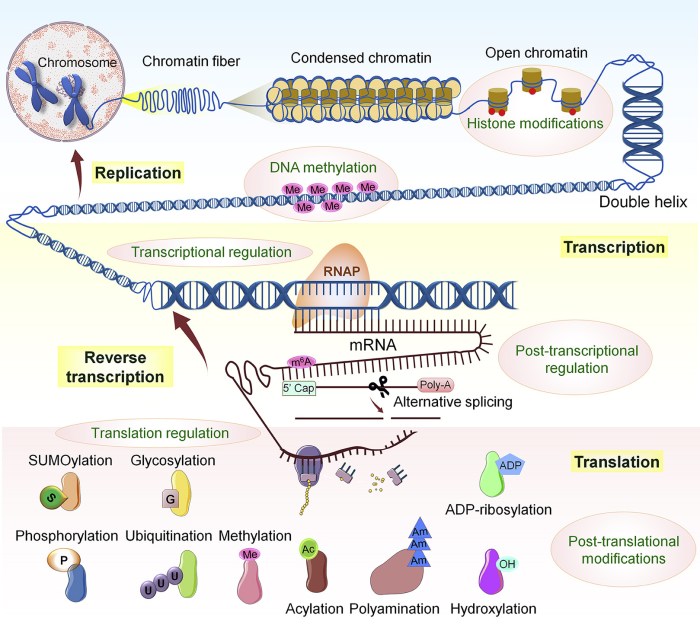
The central dogma of molecular biology is a fundamental concept that describes the flow of genetic information within biological systems. It Artikels the unidirectional transfer of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein.
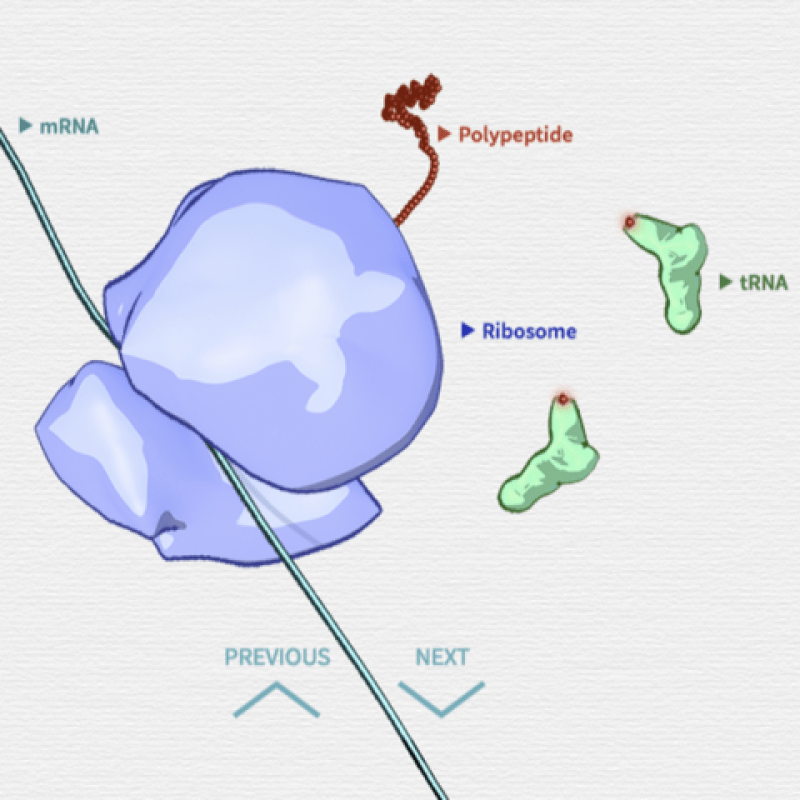
DNA, the genetic material, contains the instructions for building and maintaining an organism. Through a process called transcription, DNA is copied into RNA, which carries the genetic information to the ribosomes, where protein synthesis occurs. This process is essential for all life forms, as proteins are the workhorses of the cell, carrying out a wide range of functions.
Genetic Medicine Applications
Understanding the central dogma has revolutionized the field of genetic medicine. By deciphering the genetic code and the mechanisms involved in gene expression, researchers have gained insights into the molecular basis of diseases and developed novel therapeutic approaches.
- Gene Therapy:Involves introducing healthy genes into cells to correct genetic defects or replace faulty genes.
- Pharmacogenomics:Tailors drug treatments based on an individual’s genetic makeup, optimizing drug efficacy and reducing adverse effects.
- Diagnostics:Genetic testing allows for early detection of genetic disorders, enabling timely intervention and personalized treatment plans.
Biointeractive Answer Key
The Biointeractive Answer Key provides a comprehensive analysis of the central dogma concept. It offers detailed explanations and examples to reinforce understanding.
The answer key aligns with the central dogma by:
- Explaining the unidirectional flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein.
- Providing examples of how genetic information is transcribed and translated.
- Highlighting the role of mutations in altering genetic information.
Examples of Genetic Medicine
Cystic Fibrosis:Caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, leading to defective chloride transport in the lungs. Gene therapy aims to introduce a functional CFTR gene to restore lung function.
Huntington’s Disease:A neurodegenerative disorder caused by a mutation in the HTT gene. Pharmacogenomics can optimize drug treatment by identifying patients who respond best to specific therapies.
Methods and Procedures, Central dogma and genetic medicine biointeractive answer key
| Method | Principle | Application | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) | Amplifies specific DNA sequences | DNA fingerprinting, genetic testing | May introduce errors |
| DNA Sequencing | Determines the order of nucleotides in DNA | Genome mapping, genetic diagnosis | Expensive, time-consuming |
| Microarrays | Detects gene expression patterns | Disease diagnosis, drug discovery | Limited gene coverage |
Case Studies
Case Study 1:A patient with cystic fibrosis receives gene therapy to introduce a functional CFTR gene, resulting in improved lung function and reduced symptoms.
Case Study 2:A patient with Huntington’s Disease undergoes pharmacogenomic testing to identify the optimal drug treatment, minimizing side effects and improving disease management.
Future Directions
The future of genetic medicine holds immense potential for personalized treatments and disease prevention.
- Gene Editing:CRISPR-Cas9 technology enables precise editing of genes, offering new avenues for treating genetic disorders.
- Personalized Medicine:Tailoring medical interventions based on an individual’s genetic profile, maximizing treatment efficacy and minimizing adverse effects.
- Precision Diagnostics:Developing advanced diagnostic tools for early detection and accurate disease classification.
Quick FAQs: Central Dogma And Genetic Medicine Biointeractive Answer Key
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
The central dogma describes the unidirectional flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein, serving as the fundamental principle governing gene expression.
How has the central dogma impacted genetic medicine?
Understanding the central dogma has enabled the development of genetic testing, gene therapy, and personalized medicine, revolutionizing the diagnosis and treatment of genetic diseases.
What is the significance of the Biointeractive Answer Key resource?
The Biointeractive Answer Key provides detailed explanations and analysis of key concepts related to the central dogma, offering a valuable resource for students and researchers.